Introduction to Pointers
Pointers are variables that hold address of another variable of same data type.
Pointers are one of the most distinct and exciting features of C language. It provides power and flexibility to the language. Although pointer may appear little confusing and complicated in the beginning, but trust me its a powerful tool and handy to use once its mastered.
Benefit of using pointers
- Pointers are more efficient in handling Array and Structure.
- Pointer allows references to function and thereby helps in passing of function as arguments to other function.
- It reduces length and the program execution time.
- It allows C to support dynamic memory management.
Concept of Pointer
Whenever a variable is declared, system will allocate a location to that variable in the memory, to hold value. This location will have its own address number.
Let us assume that system has allocated memory location 80F for a variable a.
int a = 10 ;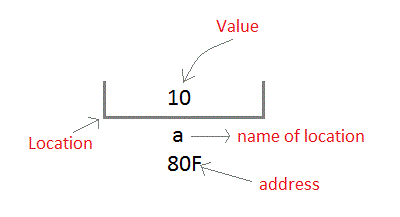
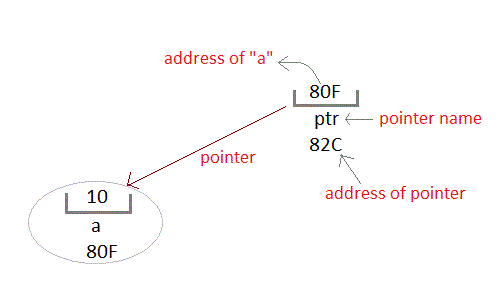
We can access the value 10 by either using the variable name a or the address 80F. Since the memory addresses are simply numbers they can be assigned to some other variable. The variable that holds memory address are called pointer variables. A pointer variable is therefore nothing but a variable that contains an address, which is a location of another variable. Value of pointer variable will be stored in another memory location.
No comments:
Post a Comment