Type Casting
Assigning a value of one type to a variable of another type is known as Type Casting.
Example :
int x = 10; byte y = (byte)x;
In Java, type casting is classified into two types,
- Widening Casting(Implicit)
- Narrowing Casting(Explicitly done)
Widening or Automatic type converion
Automatic Type casting take place when,
- the two types are compatible
- the target type is larger than the source type
Example :
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i = 100;
long l = i; //no explicit type casting required
float f = l; //no explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Float value "+f);
}
}
Output :
Int value 100 Long value 100 Float value 100.0
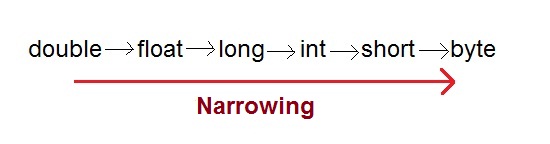
Narrowing or Explicit type conversion
When you are assigning a larger type value to a variable of smaller type, then you need to perform explicit type casting.
Example :
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 100.04;
long l = (long)d; //explicit type casting required
int i = (int)l; //explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Double value "+d);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
}
}
Output :
Double value 100.04 Long value 100 Int value 100